categorías
Contacto
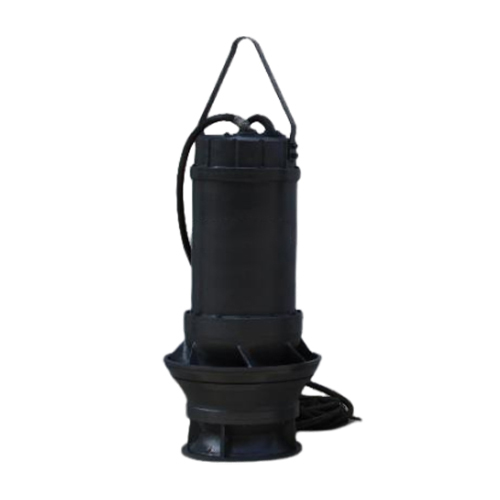

High Efficiency Submersible Axial Flow Pump
High Efficiency Submersible Axial Flow Pumps are essential components in various industrial and agricultural applications, designed to move large volumes of fluid efficiently. These pumps are characterized by their unique operating principle, which allows for high flow rates at relatively low head pressures.
Fluid Flow Direction
The direction in which fluid flows through a High Efficiency Submersible Axial Flow Pump is its distinguishing feature. The fluid enters and exits these pumps parallel to the impeller's axis of rotation. In contrast to centrifugal pumps, where the fluid enters axially but exits radially, this axial flow pattern occurs.
The unique design of the pump's components, particularly the impeller and the casing, allows for the axial flow direction. The impeller blades, which are designed to direct the flow along the pump's axis, direct the fluid as it enters the system. Compared to other pump types, this design enables the efficient movement of large volumes of fluid with little direction change, resulting in lower energy losses.
Model | Vane Angle | Capacity (m³/h) | Head (m) | Power (Kw) | Speed (r/min) | Effciency (%) | Outer diameter of impeller (mm) |
600QH-40 | 0° | 4415.2 | 14.09 | 250 | 740 | 84.1 | 550 |
700QH-72 | 0° | 5056.1 | 6.54 | 160 | 740 | 84.2 | 600 |
800QH-35 | 0° | 7257.4 | 14.71 | 400 | 590 | 85.1 | 700 |
1000QH-40 | +2° | 12461.6 | 16.52 | 710 | 490 | 86.2 | 870 |
1200QH-72 | +4° | 15607 | 8.45 | 560 | 490 | 85.8 | 950 |
1300QH-72 | -2° | 17024 | 4.4 | 400 | 370 | 84.6 | 1150 |
1400QH-72 | -4° | 15815 | 5.99 | 450 | 370 | 84.9 | 1200 |
600QZ-50 | 0° | 3690.7 | 8.84 | 132 | 740 | 83.7 | 550 |
700QZ-75 | 0° | 5451.5 | 7.33 | 160 | 740 | 83.9 | 600 |
800QZ-100 | +2° | 6513.1 | 3.99 | 132 | 590 | 84.2 | 700 |
1000QZ-135 | +4° | 12167.9 | 3.41 | 200 | 490 | 82.5 | 870 |
1200QZ-160 | -2° | 11975.7 | 2.85 | 160 | 490 | 83.9 | 950 |
1300QZ-50 | -4° | 12936.2 | 8.9 | 450 | 370 | 82.2 | 1150 |
1400QZ-100 | 0° | 16426.4 | 6.51 | 400 | 370 | 82.6 | 1200 |
1600QZ-135 | +2° | 29598.3 | 4.88 | 560 | 295 | 82.6 | 1480 |

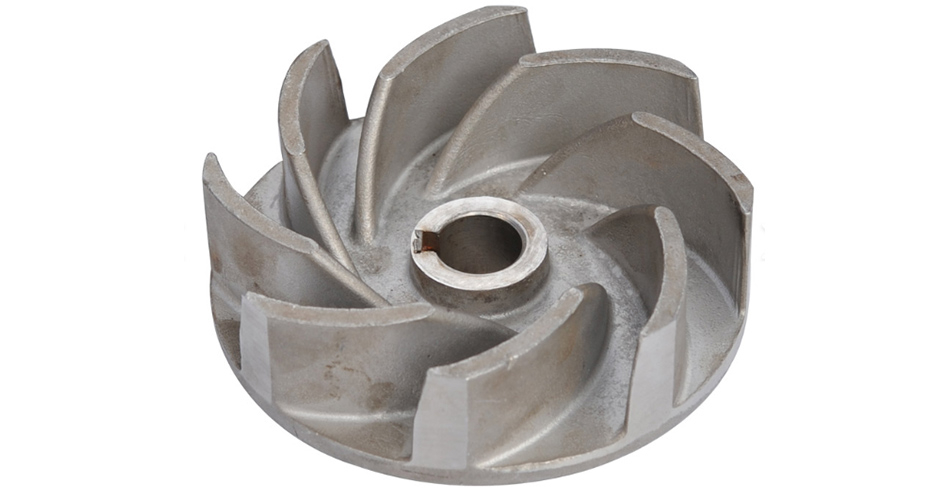
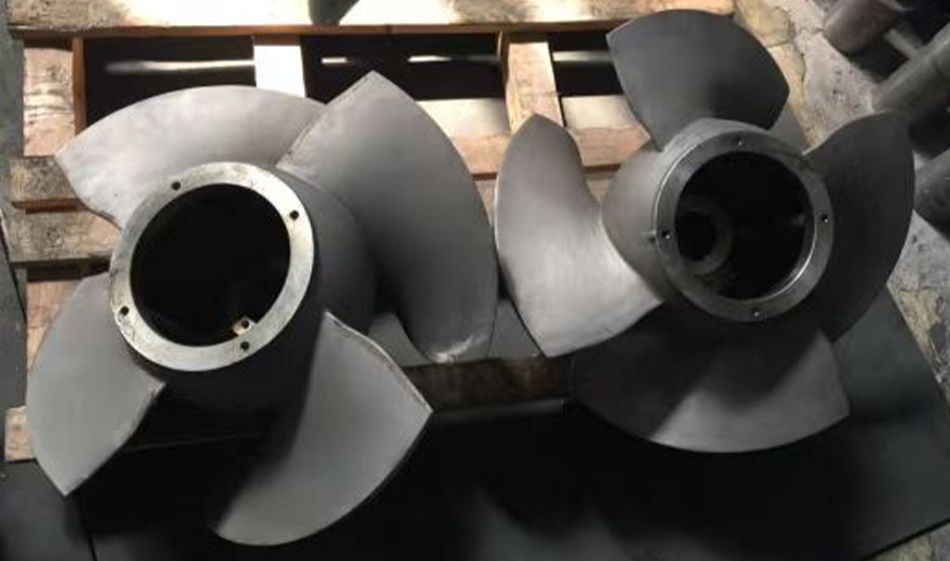
Impeller Design
The impeller is the heart of a High Efficiency Submersible Axial Flow Pump, and its design plays a crucial role in determining the pump's performance characteristics. Axial flow pump impellers are distinctly different from those found in centrifugal pumps, reflecting their unique operating principle.
The typical impeller resembles a propeller or fan blade. It consists of multiple blades arranged around a central hub, with each blade designed to guide the fluid along the pump's axis. The number of blades can vary depending on the specific pump design and application requirements, but typically ranges from three to six blades.
The blade profile is carefully engineered to optimize fluid flow and pump efficiency. The leading edge of the blade, where the fluid first contacts the impeller, is usually designed with a smooth, rounded profile to minimize turbulence and cavitation risks. The blade then curves gently, guiding the fluid through the pump while imparting kinetic energy.
One key feature of High Efficiency Submersible Axial Flow Pump impellers is their relatively small diameter compared to the pump casing. This design allows for a large open flow area, which is crucial for handling high flow rates with minimal resistance. The small diameter also contributes to the pump's compact design, making it suitable for applications where space is limited.
The angle of the impeller blades, known as the blade pitch, is a critical design parameter. It determines the balance between flow rate and pressure increase. Steeper blade angles generally result in higher head pressures but lower flow rates, while shallower angles favor higher flow rates at lower pressures. Some advanced High Efficiency Submersible Axial Flow Pump designs incorporate variable pitch impellers, allowing for adjustment of the pump's performance characteristics to meet changing system demands.
The material selection for the impeller is also crucial. Depending on the application, impellers may be made from various materials, including stainless steel, bronze, or specialized alloys. The choice of material is influenced by factors such as the corrosiveness of the pumped fluid, the presence of abrasive particles, and the required durability of the pump.


Application Areas
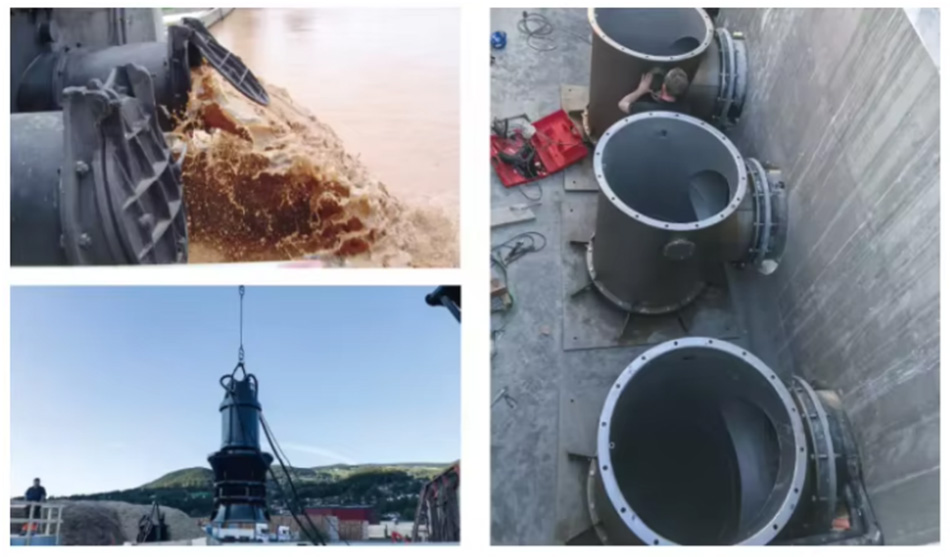
High Efficiency Submersible Axial Flow Pumps find widespread use across various industries due to their ability to move large volumes of fluid efficiently at relatively low head pressures. Their unique characteristics make them particularly suitable for certain applications where other pump types may be less effective or efficient.
One of the primary application areas for High Efficiency Submersible Axial Flow Pumps is in water management and flood control. These pumps are often used in stormwater pumping stations, where they can quickly move large volumes of water to prevent flooding in urban areas. Their high flow capacity allows them to rapidly clear excess water during heavy rainfall events or storm surges.
In agriculture,it plays a crucial role in irrigation systems. They are used to draw water from rivers, lakes, or reservoirs and distribute it across large agricultural areas. The high flow rates achievable with these pumps make them ideal for supplying water to extensive irrigation networks efficiently.
The wastewater treatment industry is another significant user of High Efficiency Submersible Axial Flow Pumps. In treatment plants, these pumps are often employed in the initial stages to move large volumes of raw sewage or partially treated water between different treatment processes. Their ability to handle fluids containing small solid particles without significant loss of efficiency makes them particularly suitable for this application.
Cooling systems in power plants and large industrial facilities frequently utilize axial flow pumps. These pumps are used to circulate large volumes of cooling water through heat exchangers, condensers, and cooling towers. The high flow rates and relatively low head pressures required in many cooling applications align well with the characteristics.
In the maritime industry, High Efficiency Submersible Axial Flow Pumps find applications in various shipboard systems. They are used for ballast water management, firefighting systems, and general seawater pumping applications. The compact design of these pumps makes them suitable for installation in the limited space available on ships.
High Efficiency Submersible Axial Flow Pumps are also used in the oil and gas industry, particularly in offshore applications. They are employed for seawater lift, providing cooling water and supplying water for injection into oil reservoirs to maintain pressure.
In the mining industry, it is used for dewatering operations, helping to remove excess water from mine sites and quarries. Their high flow capacity allows for efficient water removal, which is crucial for maintaining safe and productive mining operations.
The aquaculture industry utilizes High Efficiency Submersible Axial Flow Pumps for circulating and aerating large volumes of water in fish farms and other aquaculture facilities. The gentle handling of water by these pumps helps maintain a suitable environment for aquatic life.

High Efficiency Submersible Axial Flow Pump for Sale
Tianjin Kairun offers customization options to meet the unique needs of our customers. If you are choosing your axial flow pump manufacturers, welcome to contact us at catherine@kairunpump.com.
When considering the purchase of the pump, it's crucial to select a manufacturer with a proven track record of quality and reliability. Tianjin Kairun has established itself as a reputable supplier in the pump industry, offering a range of High Efficiency Submersible Axial Flow Pump solutions suitable for various applications.
One of the key advantages of working with Tianjin Kairun is their ability to provide customized solutions. This flexibility allows customers to obtain pumps that are precisely tailored to their specific operational requirements, potentially improving efficiency and reducing long-term costs.